Closed Grid Ultrasonic Testing (UT) Surveys in Power Stations
Power stations must run safely and reliably every day. A small defect in a boiler tube, pressure vessel, or steam line can lead to high repair costs, efficiency losses, or even unplanned shutdowns. To reduce these risks, operators often rely on Closed Grid Ultrasonic Testing (UT) Surveys.


What is a Closed Grid UT Survey?
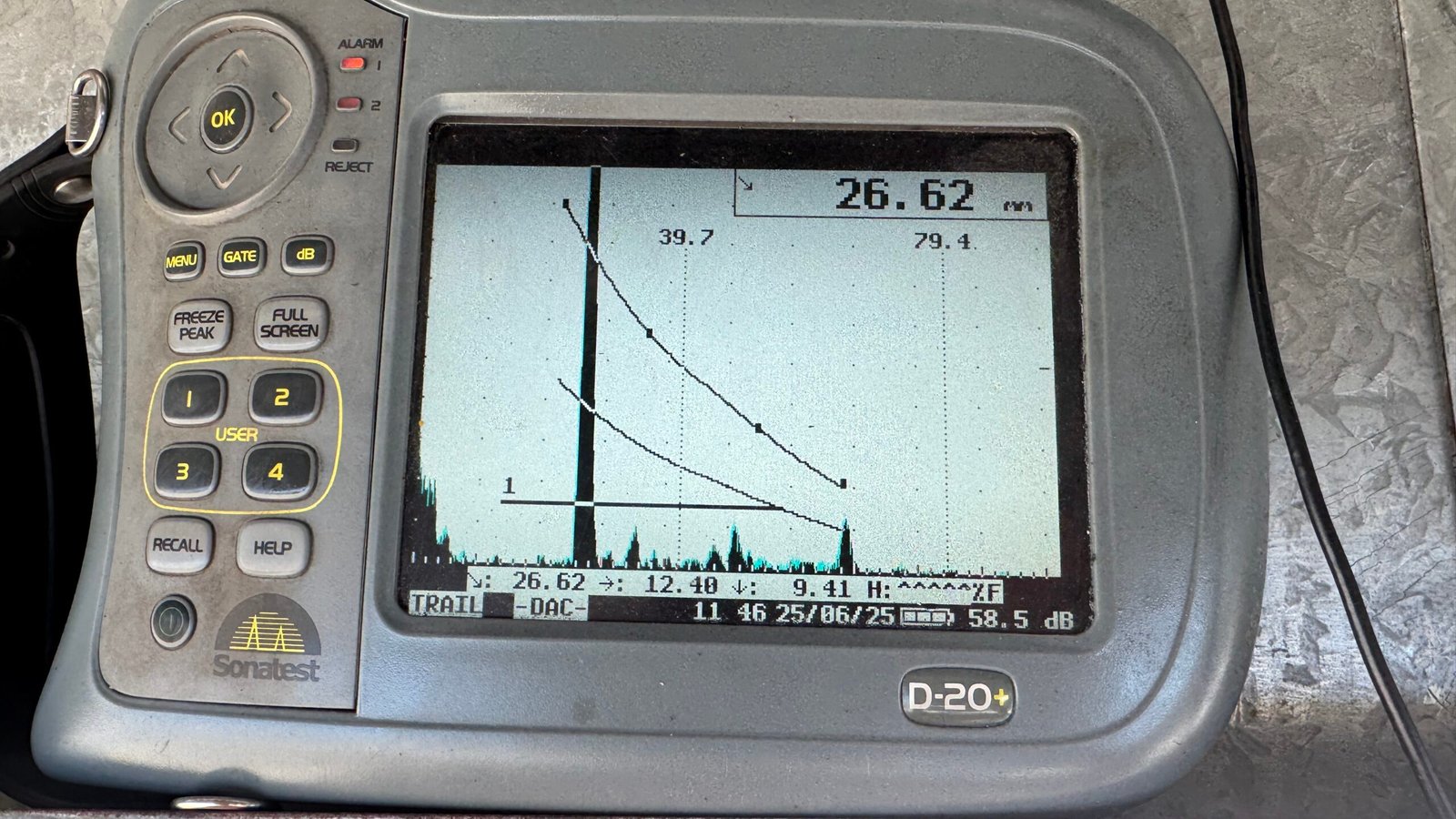
A closed grid UT survey is a method where inspectors take ultrasonic thickness readings on a mapped grid laid across the surface of a component. Instead of checking only a few random spots, this approach builds a full thickness map. As a result, engineers can see exactly where corrosion, erosion, or wall thinning is happening.
The spacing of the grid depends on the component and its risk profile. For example, a high-pressure boiler tube may need a tighter grid than a low-risk tank wall.
Why Power Stations Rely on Closed Grid UT
Power stations operate under intense heat, pressure, and mechanical stress. These conditions can accelerate wear, cracking, and corrosion in critical welds. If left unchecked, such defects may lead to safety hazards, costly shutdowns, or even catastrophic failures.
Because Closed Grid UT surveys offer a systematic and highly repeatable inspection method, they help operators detect early warning signs. Moreover, they support compliance with strict regulatory requirements, including safety standards set by international inspection bodies.
In addition, this proactive approach extends asset lifespan, optimises maintenance planning, and minimises downtime.

Benefits of Closed Grid UT Surveys
When compared with other inspection methods, Closed Grid UT offers unique advantages:
No radiation exposure – Unlike radiographic testing, ultrasonic methods avoid the risks of radiation.
High precision – Grid mapping ensures small defects, such as cracks or lack of fusion, are not missed.
Subsurface flaw detection – UT can identify internal weaknesses that surface testing methods may overlook.
Efficient reporting – C-scan images provide a visual record that can be compared over time to track deterioration.
Therefore, many operators choose Closed Grid UT as their preferred inspection method for welds and pipework in critical systems.
How Closed Grid UT Surveys Are Conducted
A Closed Grid UT survey follows a structured process:
Preparation – Inspectors clean and prepare the surface to ensure accurate readings.
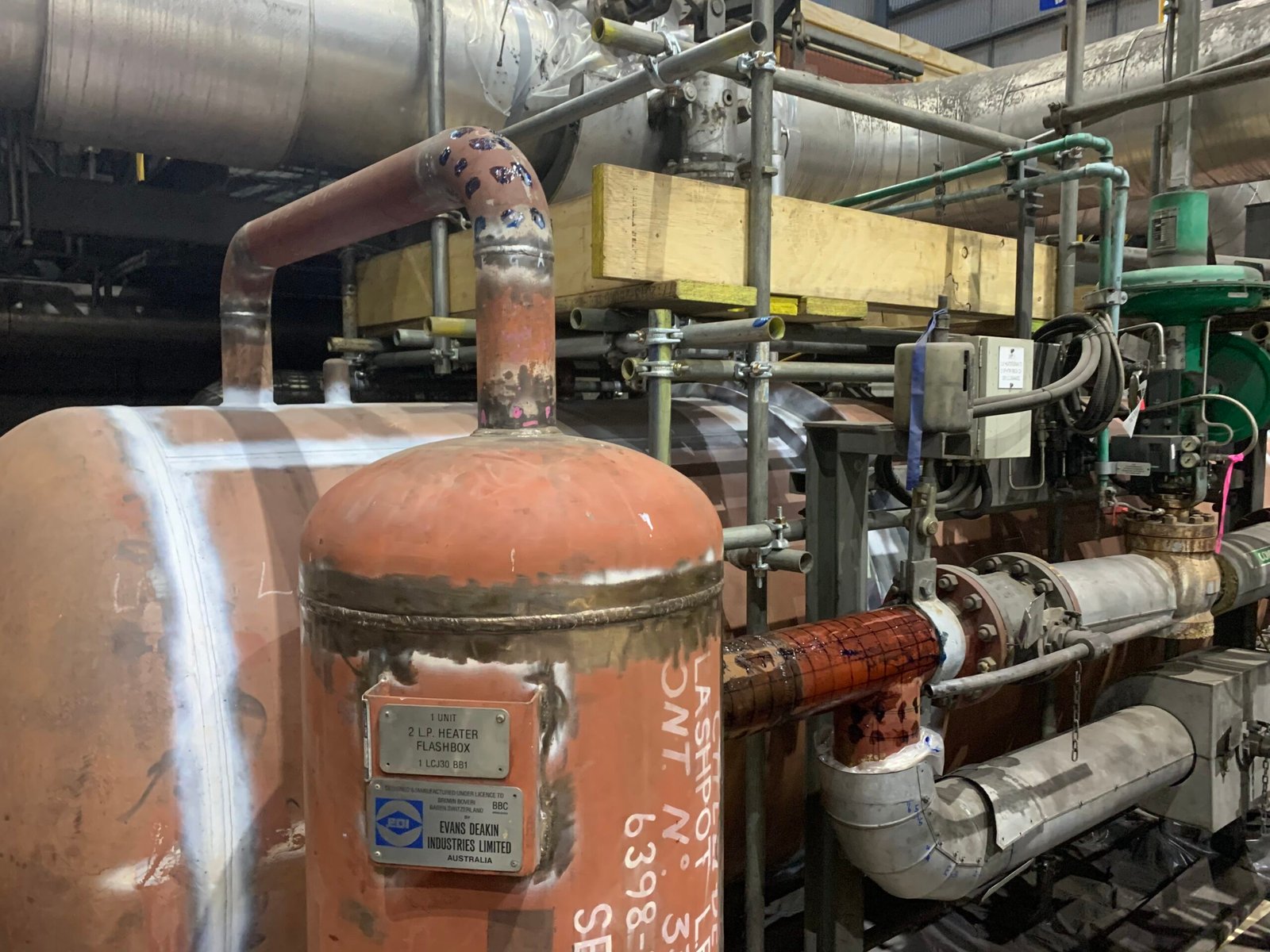
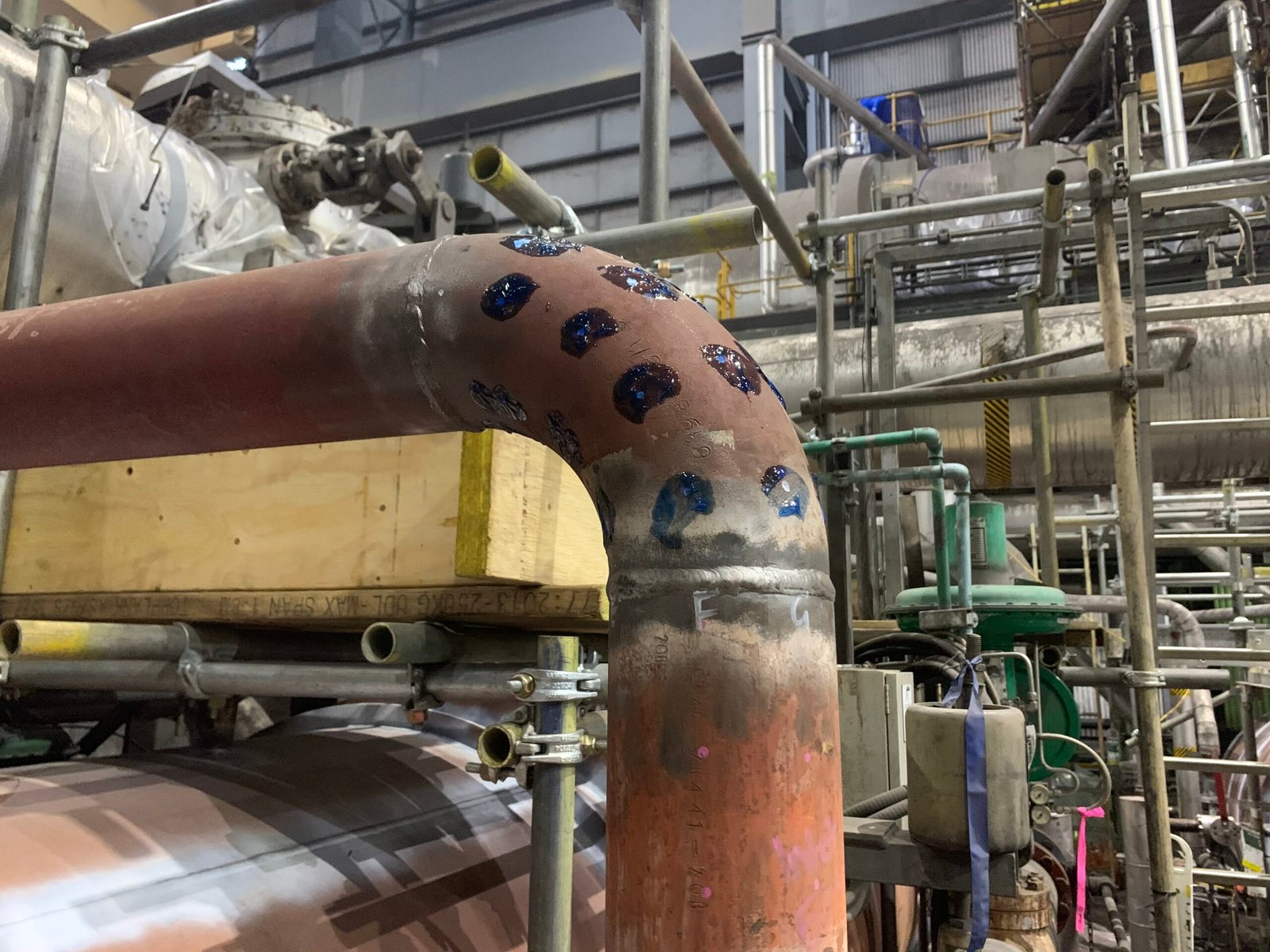
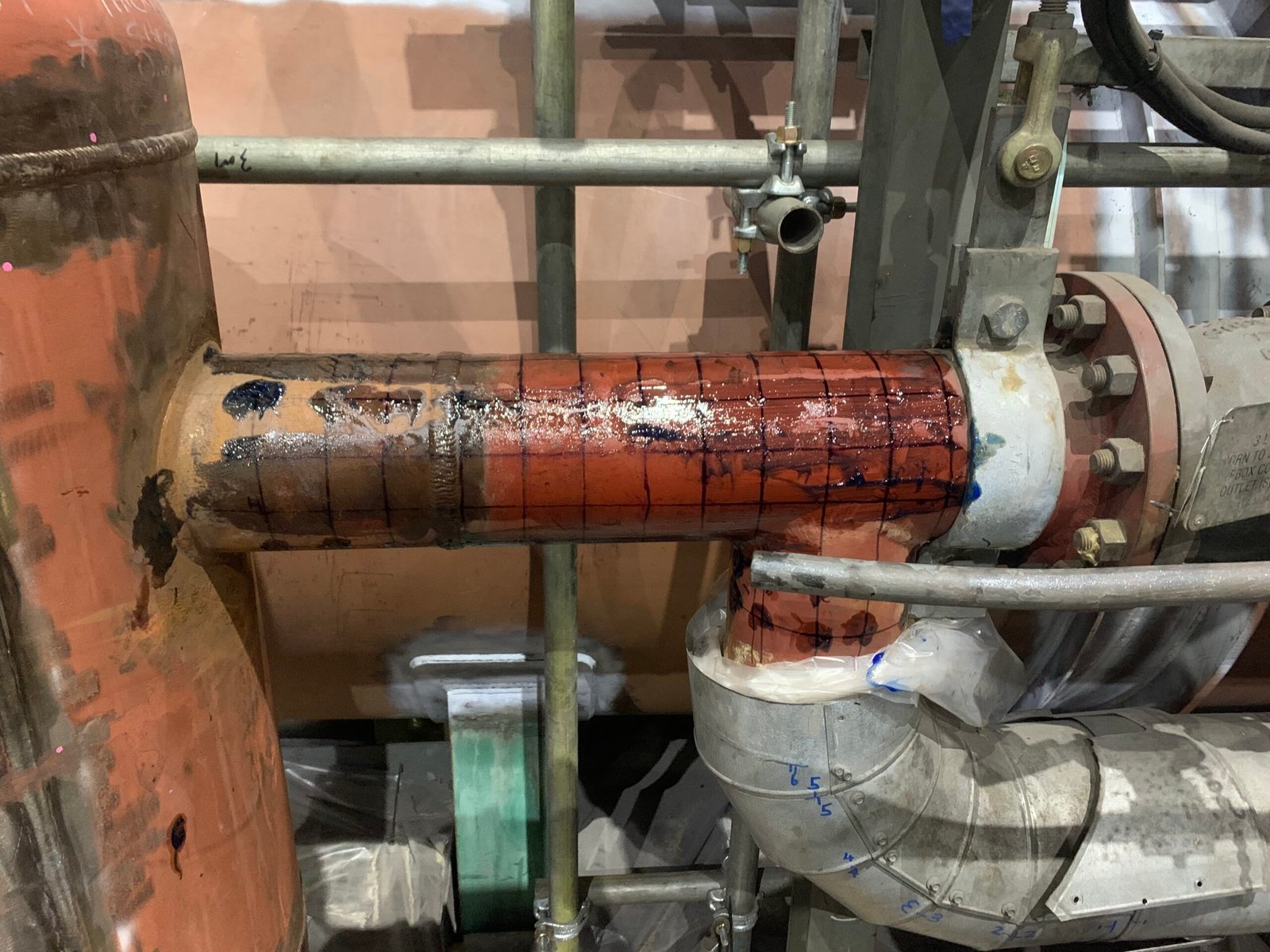
Grid Mapping – A grid is marked out on the component surface, covering the entire weld or section of pipework.
Data Collection – Ultrasonic probes are placed systematically across the grid to record thickness and flaw data.
Data Analysis – Results are compiled into a C-scan image that visually represents the internal structure.
Reporting – Engineers review and interpret the data, providing detailed insights into weld integrity and recommendations for corrective action if needed.
Because the process is repeatable, future surveys can be compared against previous results to monitor deterioration over time.
“Spot ultrasonic checks can miss localised corrosion. Closed Grid UT provides a complete thickness map, accurately identifying wall thinning and erosion patterns across the entire component.”
The Process
Preparation – Inspectors clean the surface and mark out a grid with chalk, paint, or templates.
Measurement – Each grid point is tested with an ultrasonic probe.
Data capture – Inspectors record thickness readings using digital logging equipment.
Reporting – Engineers receive colour-coded thickness maps, corrosion rate calculations, and clear recommendations.
Case Example: Detecting Weld Cracks in Power Generation
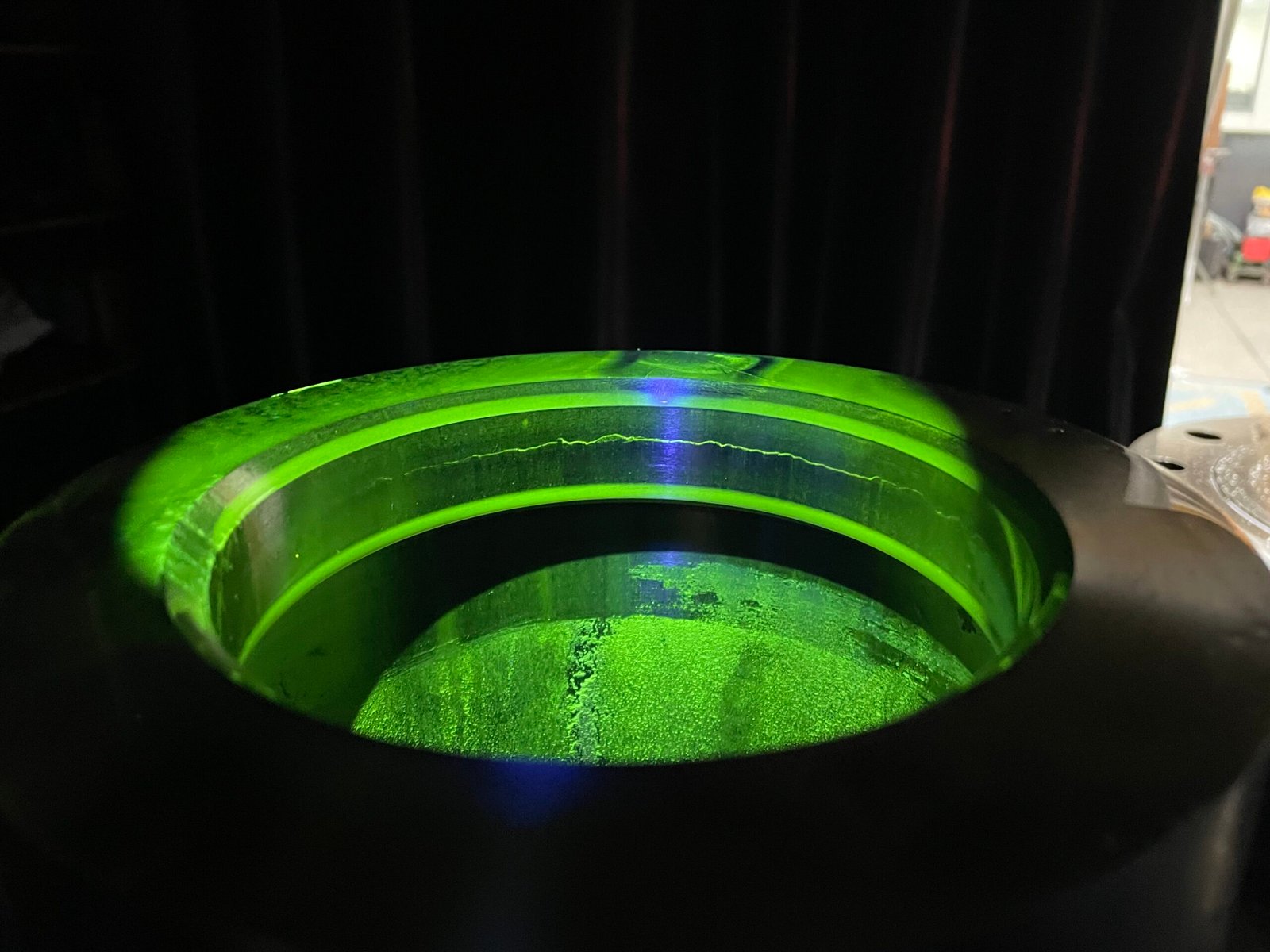
Recently, a large power station scheduled a Closed Grid UT survey on its piping. During the inspection, small areas of thinning were detected. Although these defects were not yet critical, they posed a long-term risk.
Thanks to the early detection, the maintenance team repaired the welds during a planned shutdown. Consequently, the station avoided an unplanned outage that could have cost thousands in lost production and repair expenses.
This case demonstrates how Closed Grid UT provides real-world value, not just compliance.
Conclusion
Closed grid UT surveys play a vital role in power station asset management. They not only provide accurate, repeatable data but also support safe operation, extend the life of critical equipment, and prevent costly failures.
If your facility needs detailed thickness mapping or advice on inspection planning, contact Qualiss today.
Q1. What is a Closed Grid UT Survey?
A Closed Grid UT (Ultrasonic Testing) Survey is a systematic, grid-based inspection method used to map and assess welds, pipework, and structural components in detail. It provides highly accurate thickness and flaw detection data, making it ideal for critical power station infrastructure.
Q2. Why are Closed Grid UT Surveys important in power stations?
Power stations operate under extreme temperatures and pressures. Closed Grid UT Surveys help identify early signs of cracking, corrosion, or lack of fusion in welds before they lead to costly failures or shutdowns. This ensures safety, reliability, and compliance with industry standards.
Q3. How does Closed Grid UT compare to radiographic testing?
Unlike radiography, Closed Grid UT does not use radiation, making it safer for on-site inspections. It also provides precise thickness measurements and can detect subsurface flaws without needing access to both sides of the component.
Q4. What equipment is used in Closed Grid UT Surveys?
Specialist ultrasonic testing instruments and probes are used to collect readings across a mapped grid. The data is then processed into detailed C-scan images, giving engineers a clear visual of the weld or material’s internal condition.
Q5. How often should power stations carry out Closed Grid UT Surveys?
The frequency depends on regulatory requirements, operating conditions, and risk assessments. Typically, surveys are carried out during scheduled maintenance shutdowns or when integrity concerns are identified.
Q6. Can Closed Grid UT detect all types of weld defects?
Closed Grid UT is highly effective at wall loss, corrosion, erosionand general wall thinning. However, combining UT with other NDT methods like Dye Penetrant Inspection or Radiographic Testing can provide a more complete picture if you are looking at weld testing.